About Trauma
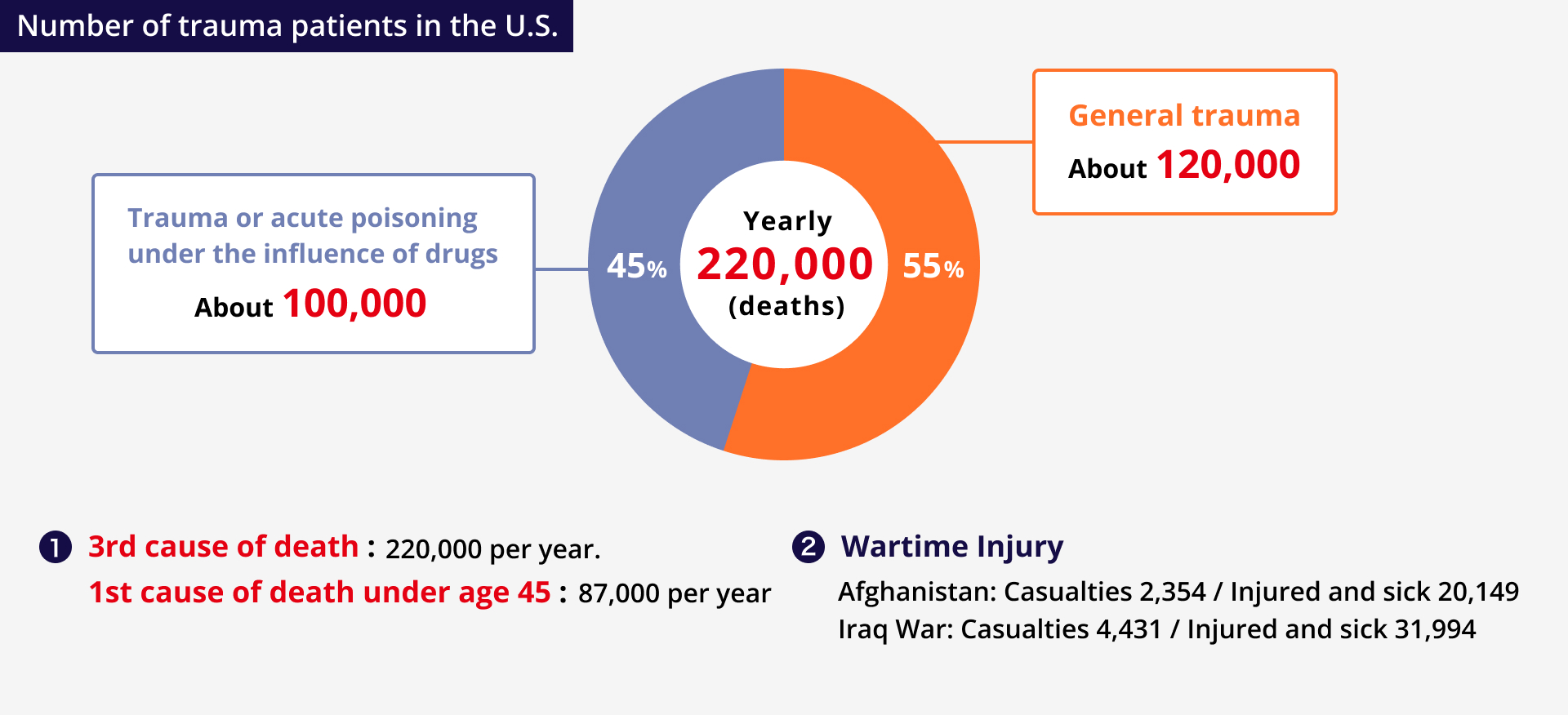
Trauma involves severe injury to tissues or organs caused by mechanical, physical, or chemical forces external to the body, causing damage to bones, muscles and tendons, nerves, blood vessels, etc., as well as ruptured internal organs. Despite heterogeneity of the origin of traumatic injury, a high percentage of patients experience hyperinflammatory activity including Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) which leads to complications such as acute kidney injury (AKI), acute lung injury, ARDS, multiple organ failure, secondary infection, sepsis, venous thromboembolism (VTE), and other secondary injury (e.g., cerebral edema). Approximately two-thirds of trauma patients will experience SIRS, and new treatments are needed to modulate the inflammatory system to reduce its associated risk, which may lead to further complications and organ injury. In the United States alone, trauma accounts for over 220,000 deaths and over 3 million non-fatal injuries per year and is the leading cause of death for people under the age of 45. The economic cost of trauma amounts to an estimated $671 billion every year, including health care and work loss for those suffering from both fatal and non-fatal injuries.
Current Treatment Methods
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) resulting from trauma is an excessive self-protective response to external stresses, including trauma (e.g., car accidents, gunshot wounds), drugs, and infection, which first results in autonomic, endocrine, hematologic, and immunologic changes.
These changes, initially intended to protect the body, become an unregulated cytokine storm, leading to a massive inflammatory cascade, organ damage, and death.
Currently, there is no effective treatment for patients who have reached this point, and only coping therapies are available for each symptom.
Healios Aims for Novel Cellular Treatments
As shown in ARDS and other clinical trials, the ability of MultiStem® to suppress inflammation in the acute phase is expected to suppress cytokine storms and have an effect on patient prognosis. In clinical trials for trauma, “MATRICS-1 study” we are conducting clinical trials with renal function as the primary endpoint to facilitate evaluation of efficacy.
MATRICS-1 study(USA)
Took control of a 156 patient, Phase 2 clinical trial in trauma
Funded almost entirely by MTEC (United States Department of Defense) and the Memorial Hermann Foundation
Conducted at University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTH) and Memorial Hermann Texas Medical Center, the busiest level 1 trauma center in the U.S.
The trauma being treated in this study is that which results from car accidents, industrial accidents, gun shot wounds, etc.
Overview:
MultiStem® for Treatment of Trauma Induced Multiple Organ Failure/Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS).
Single center, prospective, randomized, double-blind, pragmatic phase 2 clinical study.
Primary endpoint: Kidney injury stage (Day 30)
Secondary endpoint: Mortality etc.
Participant: Severely injured trauma patients within hours of hospitalization who have survived initial resuscitation
