- About Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Current Treatments
- Healios Aims for a Novel Cellular Treatment of ARDS
About Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a general term for the symptoms of acute respiratory failure arising from a number of conditions, including severe pneumonia, septicemia, and trauma.
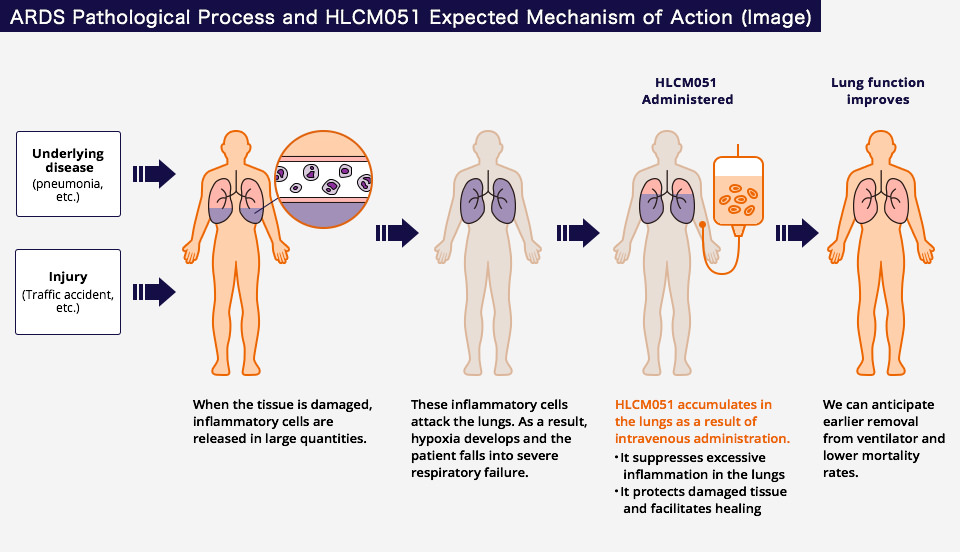
Inflammatory cells are activated in response to these diseases or injury, causing damage to the alveoli and capillaries that make up the tissue of the lungs. As a result, water accumulates in the lungs, leading to acute respiratory failure.
Typically, ARDS is said to occur within 24 to 48 hours of the onset of the illness or injury that caused it. Moreover, with a mortality rate of approximately 30 to 58% (*1), ARDS is a condition with a very poor prognosis.
The number of ARDS patients in Japan is estimated at approximately 28,000 per year.The annual number of patients worldwide is estimated to be over 1.1 million.(*2)
- *1 source: ARDS treatment guideline 2016
- *2 Estimated by Healios based on the incidence rate of epidemiological data and the total demographical population in Japan.
Worldwide is the sum of the following statistics for the U.S., Europe, and China.
USA: Diamond M et al. 2023 Feb 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–.PMID: 28613773
Europe: Community Research and Development Information Service (CORDIS) 2020 7-9
China: song-et-al-2014-acute-respiratory-distress-syndrome-emergingresearch-in-china
Current Treatments
To treat ARDS, artificial respiration using an endotracheal tube or mask is used to treat for respiratory failure in an intensive care unit. However, it is known that prolonged use of a ventilator worsens a patient's prognosis. Treatment using drugs is also provided, but at present, there are no therapeutic drugs that can make a direct improvement to a patient's vital prognosis when ARDS develops. Consequently, there is demand for new treatments for ARDS that will lead to improvements in patients' symptoms and prognosis.
Healios Aims for a Novel Cellular Treatment of ARDS
Healios has acquired the right to develop and commercialize the stem cell product MultiStem® (HLCM051), created by Athersys, for global use in the treatment of ARDS.
This cellular treatment involves an intravenous administration of HLCM051, within a certain period of time, patients diagnosed with ARDS.
HLCM051, applied intravenously to ARDS patients, accumulates in the lungs and controls excessive inflammation. Furthermore, by protecting damaged tissue and facilitating healing, it is conceivable that it could lead to improvement in lung function. Because of these effects, earlier removal from ventilation and lower mortality rates are anticipated.
Athersys conducted its exploratory clinical study of the intravenous administration of MultiStem cell therapy to treat patients who are suffering from ARDS in the United States and Europe, and announced summary results in January 2019. The study results provide further confirmation of tolerability and a favorable safety profile associated with MultiStem treatment. Importantly, MultiStem treatment was associated with lower mortality and a greater number of ventilator-free and intensive care unit (ICU) free days in the first month following diagnosis relative to patients receiving placebo.
Healios conducted a Phase II efficacy and safety trial for patients with pneumonia induced ARDS (trial name: ONE-BRIDGE). In August and November 2021, Healios announced results for the evaluation items on the 90th and 180th days after administration of HLCM051 in ONE-BRIDGE, which showed favorable results in terms of efficacy and safety. Healios decided that it will submit the Application in Japan, based on the positive results of ONE-BRIDGE study completed in Japan and the Phase II study (MUST-ARDS study) completed in the U.S. and the U.K., and on the premise that a pivotal, global Phase III trial (REVIVE-ARDS study ) of HLCM051 for ARDS, to be run mainly in the United States, would act as a confirmatory study.
